Google Scholar vs PubMed: Which Is Best for Clinical Research?
When doing research, you rely mainly on relevant and reliable sources. How do you get these? Two popular platforms you can use to access scholarly literature are Google Scholar and PubMed. But how do they compare? Which has more resources for clinical studies?
- Google Scholar Breadth: Offers a broad, interdisciplinary range of literature, making it ideal for general and expansive searches.
- PubMed Depth: Focuses on peer-reviewed, high-quality, specialized biomedical and life sciences content.
- Integrated Search: Using Google Scholar and PubMed in tandem allows you to conduct more comprehensive literature reviews.
What Is Google Scholar?
Google Scholar is a free web search engine that indexes scholarly literature from various disciplines and sources, including journal articles, theses, books, abstracts, and court opinions.
One of Google Scholar's strengths is its broad coverage across many disciplines, making it useful for interdisciplinary research. Its algorithm also prioritizes highly cited articles, identifying influential papers quickly by displaying impact through citation count.
Example of Google Scholar Search Results
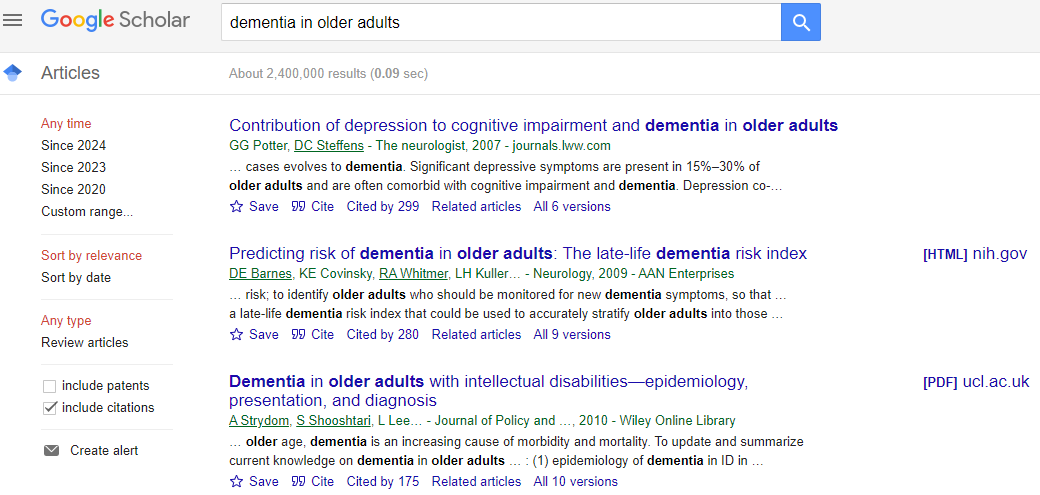
The search results include links to access full text directly from publisher websites or library links, alongside "related articles" to expand your topical search.
What Is PubMed?
PubMed is a free search engine maintained by the National Library of Medicine. It primarily accesses the MEDLINE database, focusing on peer-reviewed biomedical and life sciences topics.
With over 30 million citations from 7,000+ journals, PubMed is the specialized standard. Its key feature is the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) system, allowing conceptually related searches even if specific terms aren't in the title.
Example of PubMed Search Interface
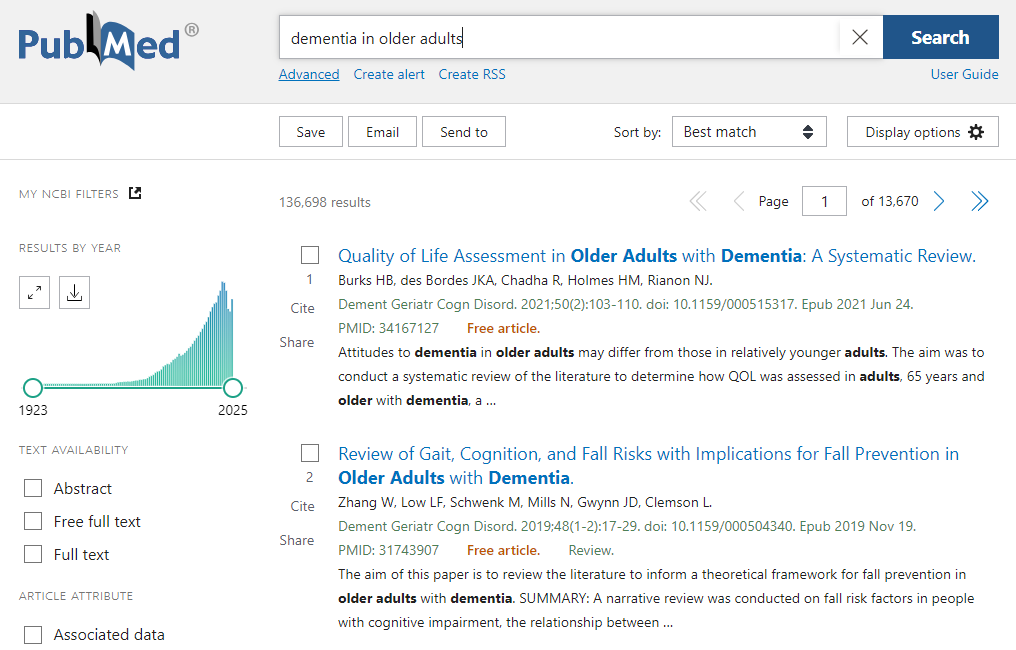
PubMed provides tools to save searches, create email alerts, and export citations to management software like Zotero or Endnote.
Which Platform Should You Use?
Choosing between them depends on your specific project needs:
Conducting Literature Reviews
PubMed is superior for targeted biomedical results thanks to MeSH indexing and advanced filters (study type, age group, etc.).
Interdisciplinary Topics
Google Scholar is better for exploring topics that bridge fields (e.g., public health and sociology) or tracking broad citation patterns.
Benefits of Google Scholar
Indexes scholarly literature from academic publishers, professional societies, and online repositories across all humanities and sciences.
Prioritizes influential papers. The "Cited by" link helps discover related research and assess a study's long-term influence in the field.
Familiar search bar and natural language processing make it intuitive, especially when jargon varies across different academic fields.

Benefits of PubMed
PubMed indexes peer-reviewed biomedical journals curated by the NLM. Key advantages include:
- Rigorous Evaluation: Only journals meeting strict scientific and editorial criteria are included.
- Advanced Querying: Supports Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), proximity searching, and truncation.
- NCBI Integration: Seamlessly connect to GenBank, ClinicalTrials.gov, and PubChem.
Effective Search Strategies
For Google Scholar
Use quotation marks for exact phrases (e.g. "clinical trial protocol") and set up alerts at the bottom of result pages for new findings.
For PubMed
Use MeSH terms for conceptual precision and use parentheses (e.g. (hypertension OR "high blood pressure") AND exercise) to group complex terms.
Optimizing PubMed for Research
Use the Advanced Search Builder to specify MeSH terms. This ensures you find the most relevant articles even if authors used different phrasing.
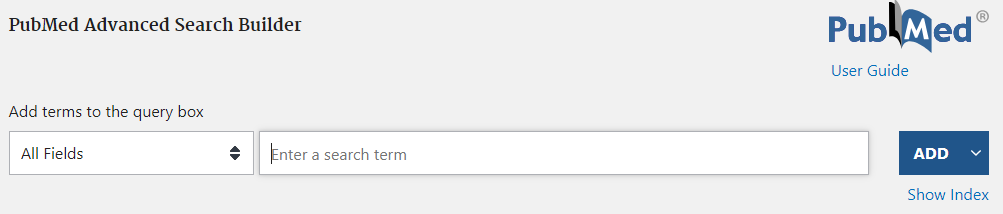
Apply filters (e.g., Randomized Controlled Trial, Publication Date within 5 years) to narrow results to the highest-quality recent evidence.
Integrating Both Platforms
- Start with PubMed: Search core biomedical literature using MeSH for conceptual synonym matching.
- Expand with Google Scholar: Look for preprints, conference proceedings, and gray literature not indexed in PubMed.
- Evaluate Rigor: Assess methodological quality, sample size, and journal reputation from both platforms before synthesis.
Reputable Health provides the tools to interpret clinical data confidently. For brands seeking to validate wellness products with clinical trials, we offer comprehensive analysis and study design services.
Book a Call TodayStay in the loop. No hype.
Evidence-based health insights and study updates, delivered weekly.
🔒 Your info is safe. We never share or sell your email.